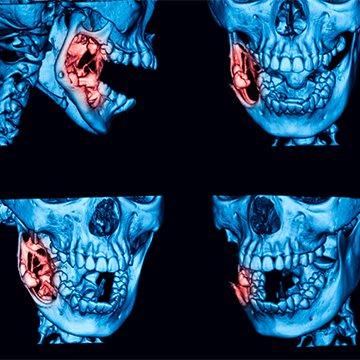
Jaw cysts and tumors are lesions that develop in the jaw bones or in the hard or soft tissues of the jaw and face. Jaw tumors and cysts are classified as odontogenic or non-odontogenic depending on their origin.
About Jaw Cysts and Tumors
They can vary greatly in shape, size and growth rates. These formations are usually benign, meaning they are not cancerous, but they can be aggressive, meaning they can expand into the surrounding hard and soft tissues, displacing or destroying these tissues.
Jaw Cysts are simply an abnormal collection of fluid surrounded by a sac of tissue. Most cysts initially develop from cells in the developing teeth. These cells are normally inactive, but can grow to form a cyst if stimulated by any stimulus.
The cyst fluid in the cyst formation accumulates and multiplies over time, so that the cyst expands and weakens or destroys the surrounding jawbone.
Jaw tumors are simply abnormal tissue growths in the jawbone. They can originate from cells involved in the formation of teeth, such as jaw cysts, or from cells that form bone, cartilage or other tissues.
Most jaw tumors are benign, but if not treated properly, they can have a devastating effect on tissues.
Treatment options for jaw cysts and tumors vary depending on the type and size of the lesion and the symptoms.
Maxillofacial surgeons usually treat these lesions with surgery alone or in combination with medical treatment.