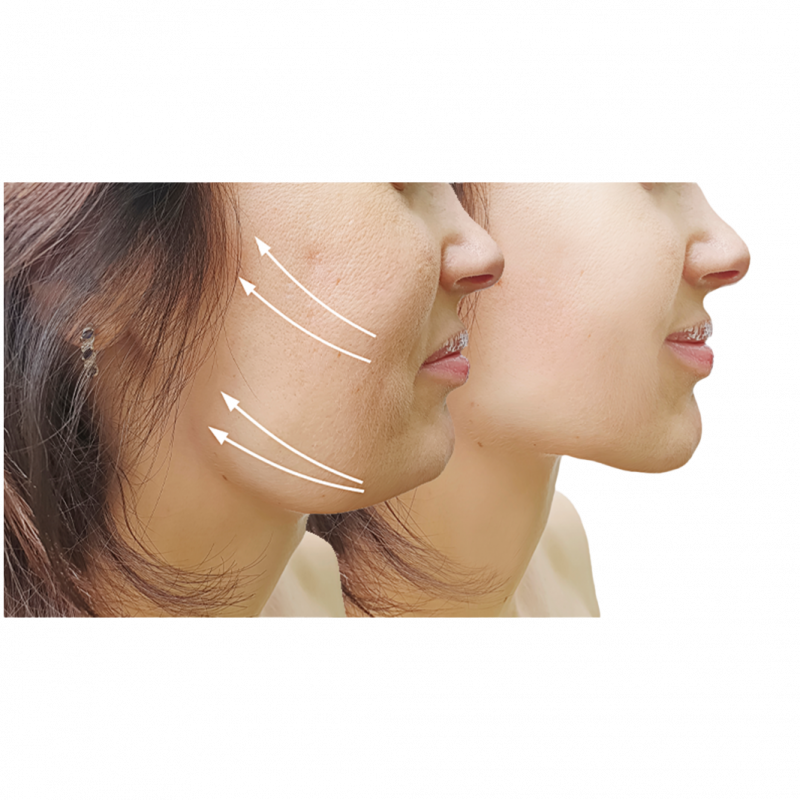
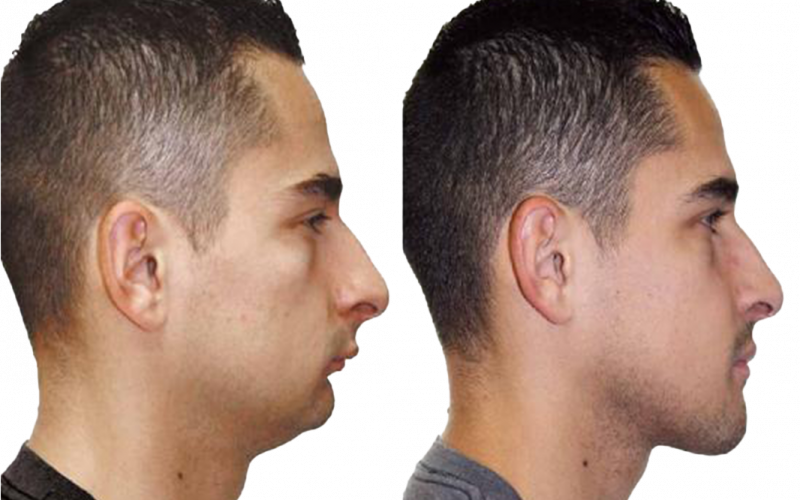
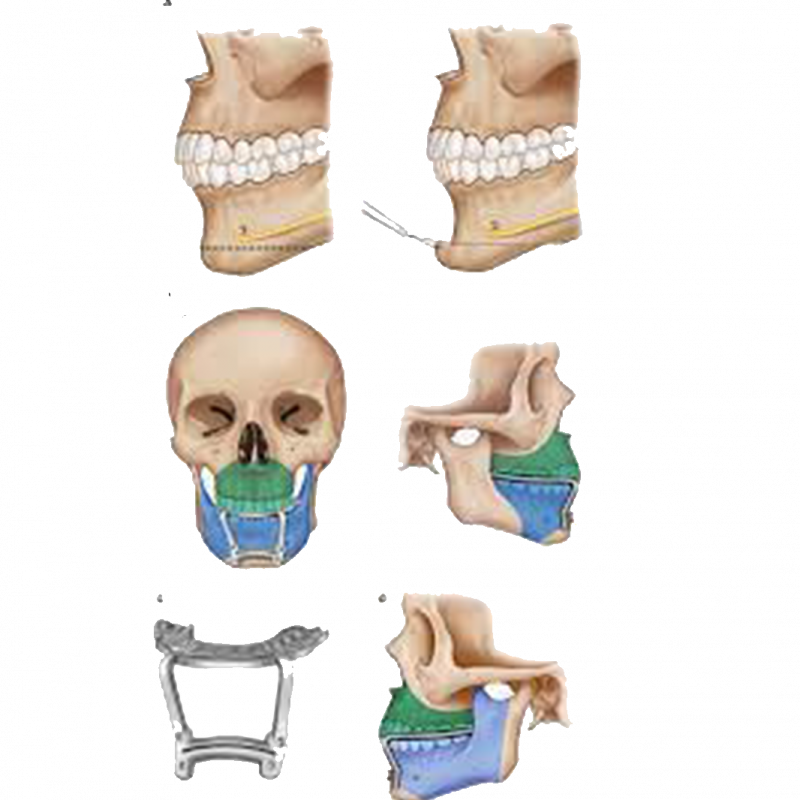
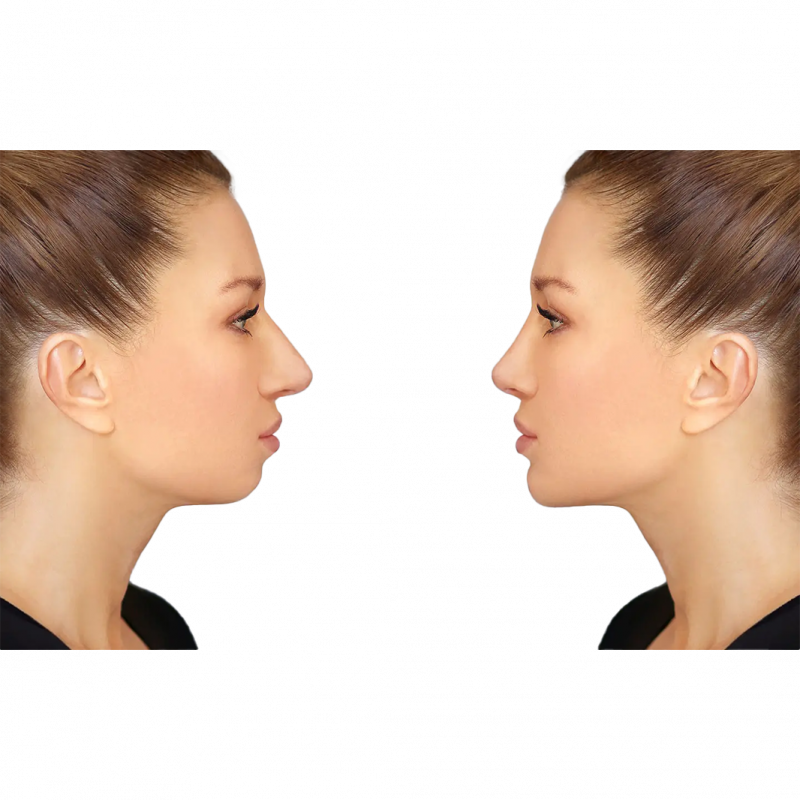Genioplasty is a type of chin surgery to realign and reshape the tip of the chin. The maxillofacial surgeon creates an incision line in the anterior part of the mandible (lower jaw) and fixes this jawbone segment with plates or screws in the planned manner by shifting it forward, backward or sideways. This procedure is performed in conjunction with orthognathic surgery in patients whose jaws are not symmetrical or incompatible with the rest of their facial features, or alone in patients who only have complaints about the tip of the chin.
What is Genioplasty?
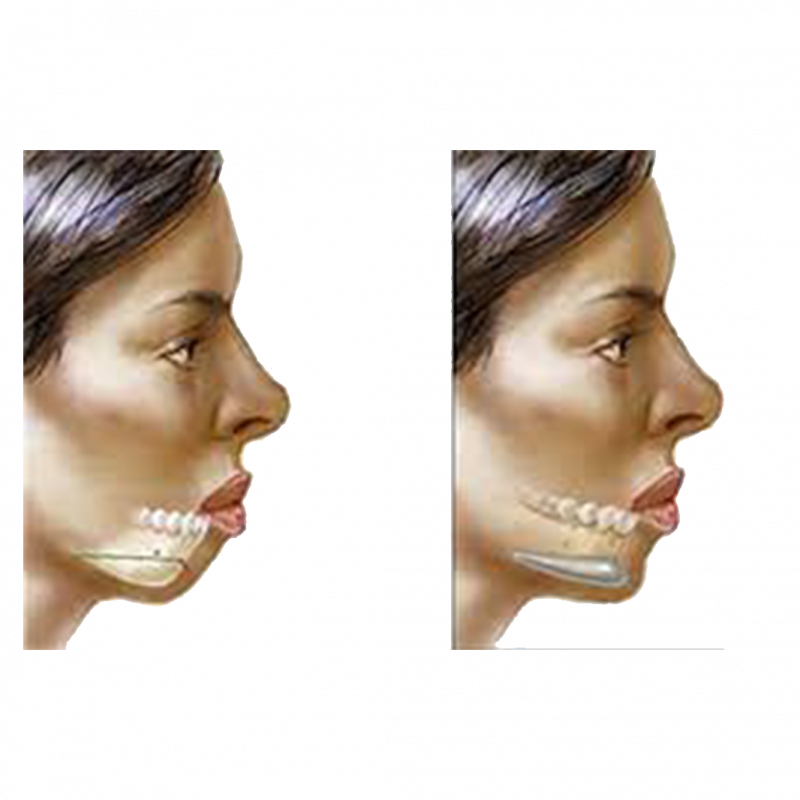
Genioplasty is a type of surgery that repositions the jaw by cutting and moving part of the lower jawbone. The procedure is performed in patients whose lower jaw is too far back or too far forward. In addition, a very long or short chin can be corrected with this intervention.
What is the Difference between Genioplasty and Chin Implant?
Genioplasty and Chin Implant are types of genioplasty (jaw repair). These interventions can both improve the appearance of the chin and help the jawline look more harmonious with the rest of the face.
The two procedures have important differences:
Genioplasty uses the patient’s existing jawbone to reshape a protruding, recessed or misaligned jaw.
With a chin implant, a small chin is enlarged by means of implant material. A flexible piece of silicone is usually used to define the lower face and jawline.
Which patients undergo genioplasty?
Most patients want to have genioplasty for aesthetic reasons. However, some people may need this procedure to reconstruct their chin and jawline. Reconstructive surgery may be necessary after an injury such as a facial fracture or if there is a congenital deformity (birth defect).
In which cases is genioplasty performed?
- Chin Asymmetry (a crooked chin that is not aligned with the center of the face)
- Jaw Length Anomalies (long or short jaw)
- Macrognati (big jaw)
- Micrognathia (small jaw)
- Prognathia (the chin protrudes too far forward)
- Retrognathia (chin too far back)
Only in the patient for the genioplasty surgery to be performed;
- Absence of a systemic disorder that prevents surgery
- Absence of skeletal jaw disorder
- No smoking
- The patient must have reached full skeletal maturity (complete bone development = late puberty)
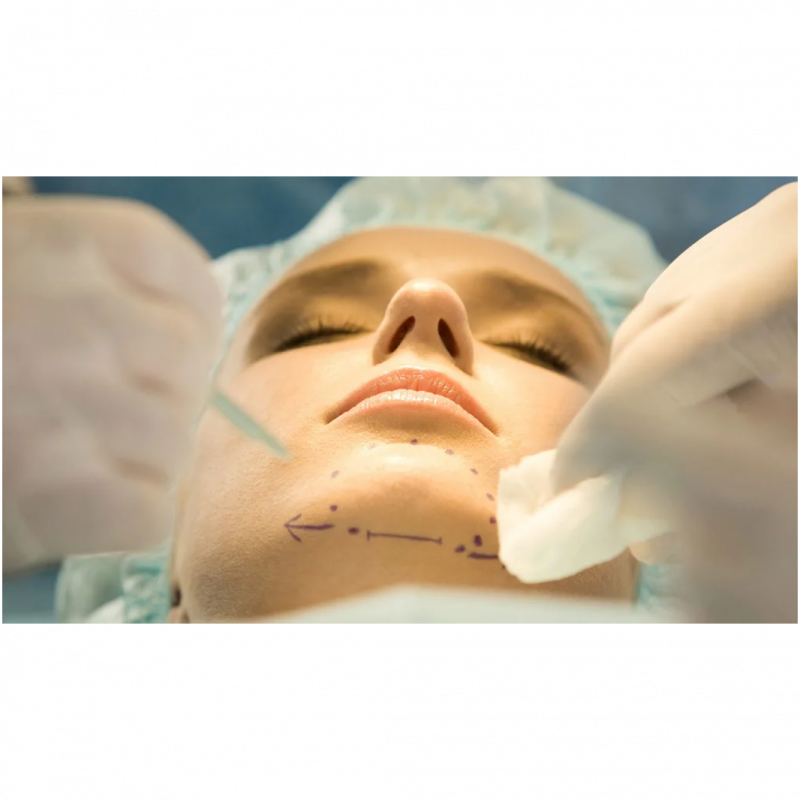
Such advanced surgical interventions are performed under general anesthesia (full unconsciousness).
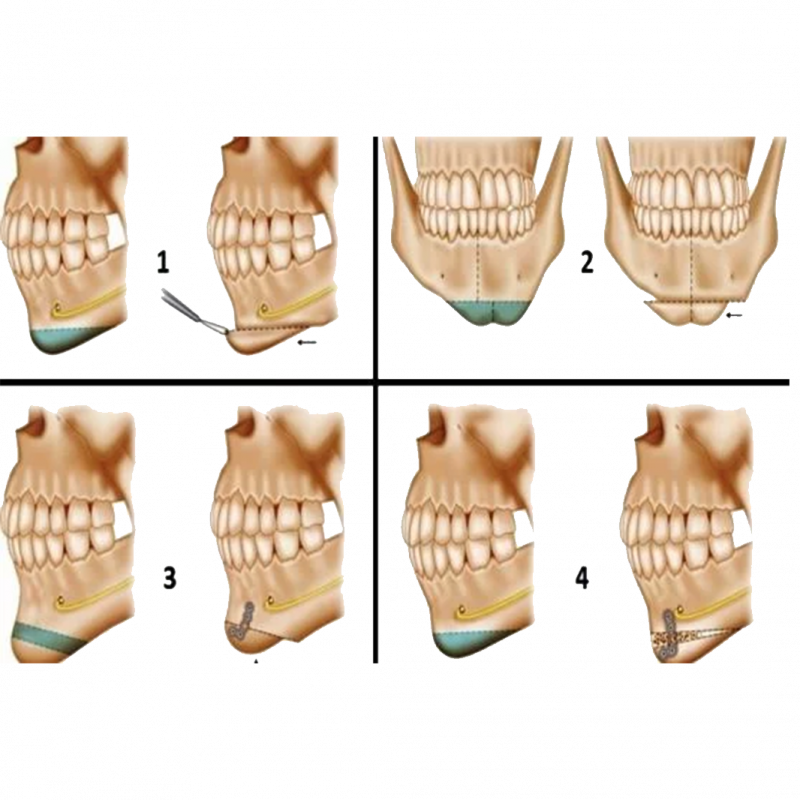
During the procedure, a horizontal incision is made intra-orally (intra-oral approach) at the base of your jawline. Since the incision scar will be inside your mouth, it will not be visible from the outside. A surgical drill is used to cut part of your jawbone.
Depending on the type of jaw realignment determined before surgery, the mobile bone segment can be moved forward, backward or sideways.
Shortening a long jaw is known by removing the cut piece of bone. To lengthen a short chin, you can leave a gap between the two parts of your jawbone.
The cavity is then filled with bone. If the gap is too large, bone can be taken from the hip bone and added.
Using wire, plates or screws, the cut bone segment is fixed to the jaw and the surgical site is closed with intraoral sutures. They apply a tape-like surgical dressing or bandage across the incision inside the mouth. You can also apply a supportive bandage on the outside of your mouth, just below your lower lip and under your chin (to reduce edema)
What happens after Genioplasty?
You can go home on the day of your surgery. Some patients may need to stay overnight in hospital. Your surgeon will give you specific instructions on how to care for your incision.
It is important not to disturb surgical dressings or stitches inside your mouth.
Your surgeon removes the dressings three to four days after the procedure.
The stitches are removed within 7-10 days if they are not resorbed, and if they are resorbed, they dissolve spontaneously within a few weeks.
RISKS / BENEFITS
What are the risks of genoplasty?
- Post op (after surgery) bleeding.
- Hematoma- bruising- blood collection under tissue)
- Infection
- Scarring (intraoral)
- Tingling or numbness in your jaw or lower lip. (Paresthesia)
What are the benefits of Genioplasty?
Genioplasty can improve the balance and symmetry of your facial features. It can also correct jaw deformities associated with birth defects, trauma or other surgeries.
What are the symptoms after genioplasty surgery?
Recovery from Genioplasty can take several weeks. You should avoid strenuous activities for a few days after the procedure. You may notice edema (swelling) and hematoma (bruising) for up to two weeks.
A diet of liquid or soft foods is recommended for a few days after surgery. Avoid hard or grainy foods, as these can irritate the wound site.
Rinsing your mouth with salt water before and after eating (if you do not suffer from hypertension) keeps your incision site clean.
Discomfort after genioplasty is usually mild, and prescribed medications should be used completely and regularly.
Cold ice compresses can reduce discomfort.
Sleep with your head over your heart to reduce swelling in your jaw and lips.
Normal activities such as exercise and work can be resumed 7 to 10 days after surgery.